Investors are relying more on ESG reporting and metrics to conduct research to gain investment-critical insights. They rely on this insight to satisfy their investors and stakeholders by ensuring that they provide good investment opportunities, with low risk. A study by Nordea Equity Research reports that between 2012 and 2015, organisations with high ESG ratings outperform the lowest rated organisations by as much as 40%. But, how do we effectively monitor and validate Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) data? How do we detect greenwashing - malicious, misleading, or simply vague or unsubstantiated? This question becomes especially pertinent when dealing with sparse data, unreliable sources, or frequent methodological changes in reporting. Traditional approaches, while valuable, often struggle to adapt to the dynamic nature of ESG reporting and the subtle ways companies might engage in greenwashing.
The Challenge of ESG Analysis
Consider this scenario: A company changes its carbon accounting methodology. Traditional systems might flag this change, but can they effectively evaluate whether this represents a genuine improvement in measurement or an attempt to obscure unfavourable data? This is where the limitations of conventional, rule-based approaches become apparent.
The challenge becomes even more complex when companies operate across multiple countries and sectors. ESG reporting requirements and materiality frameworks often don’t align across different regulatory environments, creating a tangled web of data that analysts must navigate.
Enter InferESG
In response to these challenges as part of a RegTech innovation competition by FinTech Scotland, we developed InferESG (an evolution of our InferGPT research work), an innovative solution that transforms how analysts interact with ESG data. Rather than attempting to automate the entire analysis process, InferESG serves as an intelligent assistant that augments human expertise through three key capabilities:
1. Comprehensive Report Analysis
The system begins with a thorough analysis of a company’s sustainability report, examining environmental targets, social initiatives, and governance structures. Think of it as having a highly efficient research assistant who can quickly digest hundreds of pages of documentation and highlight areas that warrant further investigation.
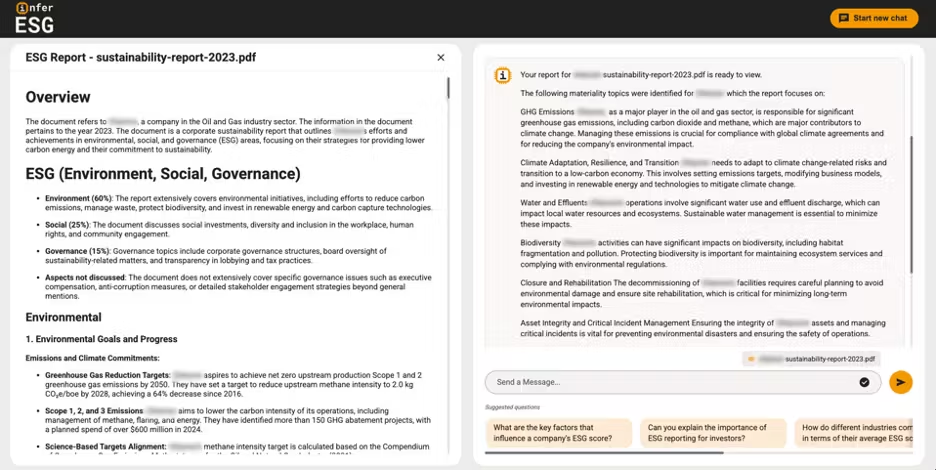
2. Interactive Investigation
Through a conversational interface, analysts can explore ESG data using natural language queries. For instance, an analyst might ask, “How does this company’s emission reduction claims compare to their actual performance over the past five years?” The system processes these queries through its multi-agent framework, providing comprehensive, evidence-based responses.
3. Evidence-Based Analysis
Every conclusion drawn by the system is supported by clear evidence trails. This transparency is crucial - it’s not enough to flag potential greenwashing; analysts need to understand how and why these conclusions were reached.
The Technical Innovation
At the heart of InferESG lies a multi-agent architecture. Rather than relying on a single AI model, the system employs specialist agents that work together to analyse ESG data. This approach allows for more nuanced analysis and better adaptation to evolving ESG standards.
The system employs a “scratchpad” feature that maintains a detailed record of its reasoning process. This creates a transparent audit trail that analysts can follow to understand exactly how conclusions were reached.
Real-World Validation
We put InferESG through its paces with rigorous testing, focusing on two companies with different ESG profiles: one from the pharmaceutical sector and another from the energy sector. The results were encouraging. When analysing sustainability reports, the system demonstrated high precision (up to 100%) in identifying potential greenwashing and ESG concerns, while maintaining strong recall (up to 96%) across different industry contexts.
Environmental Considerations
It would be remiss not to address the environmental impact of AI-powered solutions like InferESG. The current implementation, being an alpha-status research project, uses multiple LLM calls per interaction - potentially up to 10 times more energy consumption than a simple chatbot interaction. However, future optimisations through caching, knowledge graphs, and more efficient language models could significantly reduce this impact.
Looking Forward
The development of InferESG represents a significant step forward in ESG analysis, but it’s just the beginning. As ESG reporting requirements continue to evolve and new analytical techniques emerge, the open-source nature of InferESG ensures it can adapt alongside the rapidly changing landscape of sustainable investment.
As Alexandre Popa from Aberdeen noted during testing: “This solution would help someone who doesn’t have detailed knowledge of the company understand the key sustainability and material issues, and for someone who does know a company investigate them in more detail.”
By combining human expertise with advanced AI capabilities, we’re demonstrating how technology can enhance rather than replace human judgement in complex analytical tasks. The future of ESG analysis isn’t about replacing analysts with AI - it’s about giving them better tools to tackle an increasingly complex challenge.
If you’re interested in learning more about InferESG or would like to contribute to its development, you can contact us at sustainability@scottlogic.com and feel free to check out the project on GitHub: https://github.com/ScottLogic/InferESG

